Installing & Configuring Logwatch On Debian/Ubuntu, Fedora 6, CentOS 6, RHEL 6 & Arch Linux
Prerequisites
All you require for this guide in particular is a VPS or server running one of the Linux operating systems included in the title. It is possible to complete it with a sudo user although the context of this post is done using a root account. So we are presuming you have some form of root access for this. If you are in need of hosting Hoverdata provide several packages with afforable payment plans for a shared host, VPS, or dedicated server.
Introduction
Logwatch is one of many monitoring and reporting programs to be found in the Linux world. It has an emphasis on being customisable to the user’s needs whilst still being adept at analysing then summarizing log files. In this post we cover setting up the basic cycle of daily log summaries in the form of external emails to a chosen address. The program reports back on all running services by default but can be altered to only show set services if desired.
Read on to see how to get Logwatch up and running.
Download Logwatch through your Linux distribution’s package manager to begin the installation and configuration.
Debian/Ubuntu
|
1 |
apt-get install logwatch |
Fedora, CentOS , RHEL
|
1 |
yum install logwatch |
Arch Linux
|
1 |
pacman -S logwatch |
Step 2 — Postfix Configuration
Postfix is a Mail Transfer Agent (or MTA) that Logwatch depends upon for sending its mails whether internally or externally. It comes as part of the Logwatch dependencies when you download it. In this case we only have to complete two stages of the postfix configure process.
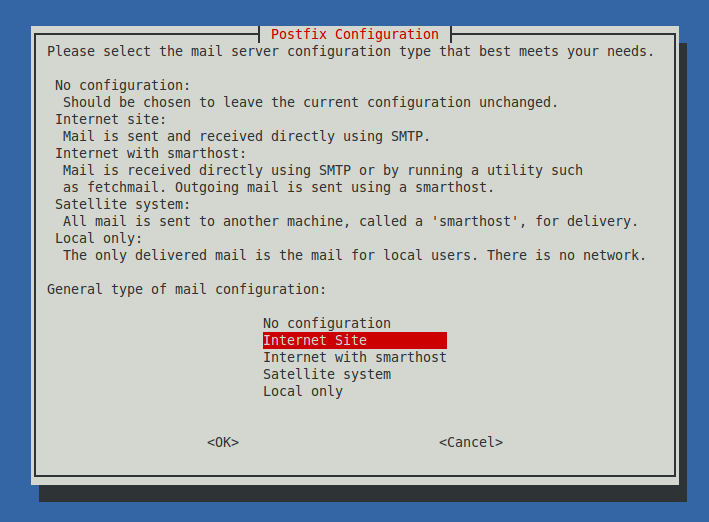
Internet Site
Select the Internet Site for our VPS/server on the first screen.
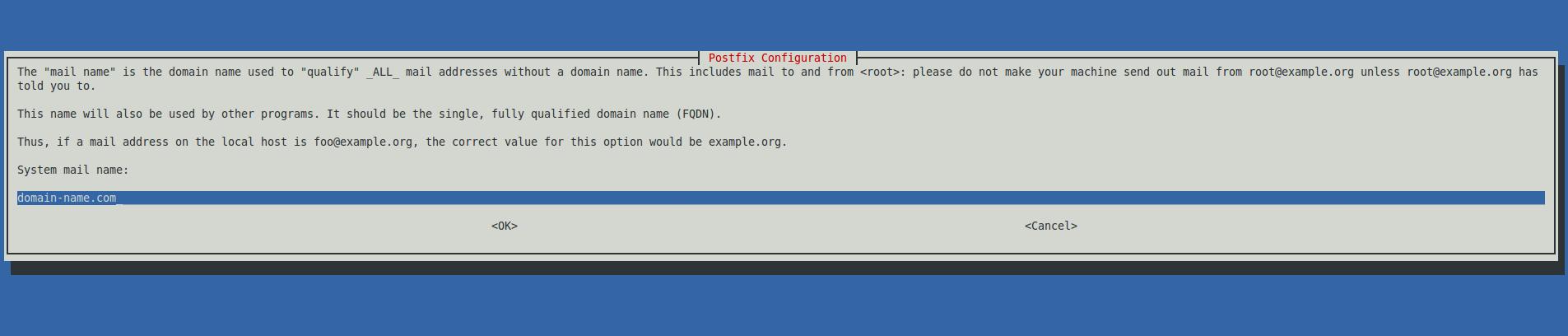
Domain Name
This should be a domain name for the VPS/server you are installing on that has a valid DNS record. For our purposes however for use with Logstash it is not imperative that you input a domain name. The format should also be of a Fully Qualified Domain Name (except you don’t need the final period).
if you are unsure what to enter for this or don’t have a valid domain name, you can just use the machine’s hostname like so: hostname.com
These two sections are usually enough for Logwatch to work with postfix without error, although this could depend upon your overall postfix setup. If using it elsewhere.
Step 3 — Logwatch.conf
As with many Linux programs the core settings of Logwatch are placed in one single config file located at:
/usr/share/logwatch/default.conf/logwatch.conf
Using any text editor open the file for writing and take a look at the contents. I’ll be using vim in the example.
|
1 |
vim /usr/share/logwatch/default.conf/logwatch.conf |
There are a number of different entries you can set in here, only a select few are completely necessary though.
- Output
- Format
- MailTo
- MailFrom
- Detail
Let’s go through these one by one in the next steps.
Step 4 — Output Directive
As we are setting up Logwatch to send us updates and reports through email we need to set this option to “mail” and not “stdout” (standard output) so reports are not fed to the command line and instead emailed.
Set it like this:
|
1 |
Output = mail |
Step 5 — Format Directive
This option lets us choose what format we want to receive the data in. It can be either HTML or plain-text. Choose “html” or leave it as “text” if you prefer text formatting.
I’ll be changing it to HTML in this example.
|
1 |
Format = html |
Step 6 — MailTo Directive
This one you’ll set to the address you want the email reports to go to once they are requested by yourself or any scripts.
|
1 |
MailTo = your-email@mail-domain.com |
Step 7 — MailFrom Directive
Now with this directive you can set the identity of who the email reports originate from. It can be a local Linux system account or an email address once again.
|
1 |
MailFrom = your-email@mail-domain.com |
Step 8 – Detail Directive
You can explicitly state what level of detail you want the email reports to take.
With either Low, Med, or High assigned to the directive.
For my example I’m setting it to Medium.
|
1 |
Detail = Med |
Step 9 — Running & Testing Logwatch
After closing and saving the config file all the changes will be made and we can start making sure everything works properly.
The easiest way to test Logwatch is to run it with no parameters on the command line and then check your specified email account.
|
1 |
logwatch |
Important: Check the email account’s spam/junk folder for the report email(s) before assuming something is not configured properly.
If even after checking your inbox there are no emails to be found then re-open the config file for Logwatch and double check all directives for errors or misplaced characters. Consult your firewall if you have one to ensure it is not blocking any sending/receiving of the emails by Postfix.
Conclusion
Everything is now set to send daily log reports to the email address. You can also set up a cronjob to run logwatch every now and then if you prefer not to make use of the config file directives, but make sure to disable the daily send directive in Logwatch first.
This other post covers how to set up cron-jobs if you need it: Cron Automation in Linux & Unix Systems
Any problems or troubleshooting should include your postfix configuration, as problems there can impact on Logwatch not sending/receiving properly. Especially if you have setup Postfix for other uses elsewhere.
Thanks for reading and ask any questions in the comments as usual.